Thank you! Your submission has been received!
Oops! Something went wrong while submitting the form.
As businesses continue to embrace cloud technology, establishing resilient and standardised cloud foundations help reduce organisational complexities and promote flexibility, security and efficiency. AWS offers a methodical approach to building the groundwork for deploying workloads.
To recap from our previous post, a landing zone is a well-architected environment that is highly scalable and secure. It is your cloud foundation, designed according to a set of best practices and guidelines.The key elements that make Landing Zones the solid foundation for your AWS environment include:
Each key element provides you with a set of guidelines and questions to consider when designing your Landing Zone.
Landing zones offer a set of best practices and architectural patterns that enable your organisation to scale. Without landing zones, businesses often struggle to enforce security standards and lack good visibility into the delivery process. Workloads often share accounts, increasing the risk of data exploits due to overly permissive policies and a lack of an audit trail. Therefore, the implementation of AWS Landing Zones for your organisation is crucial, as it helps you achieve:
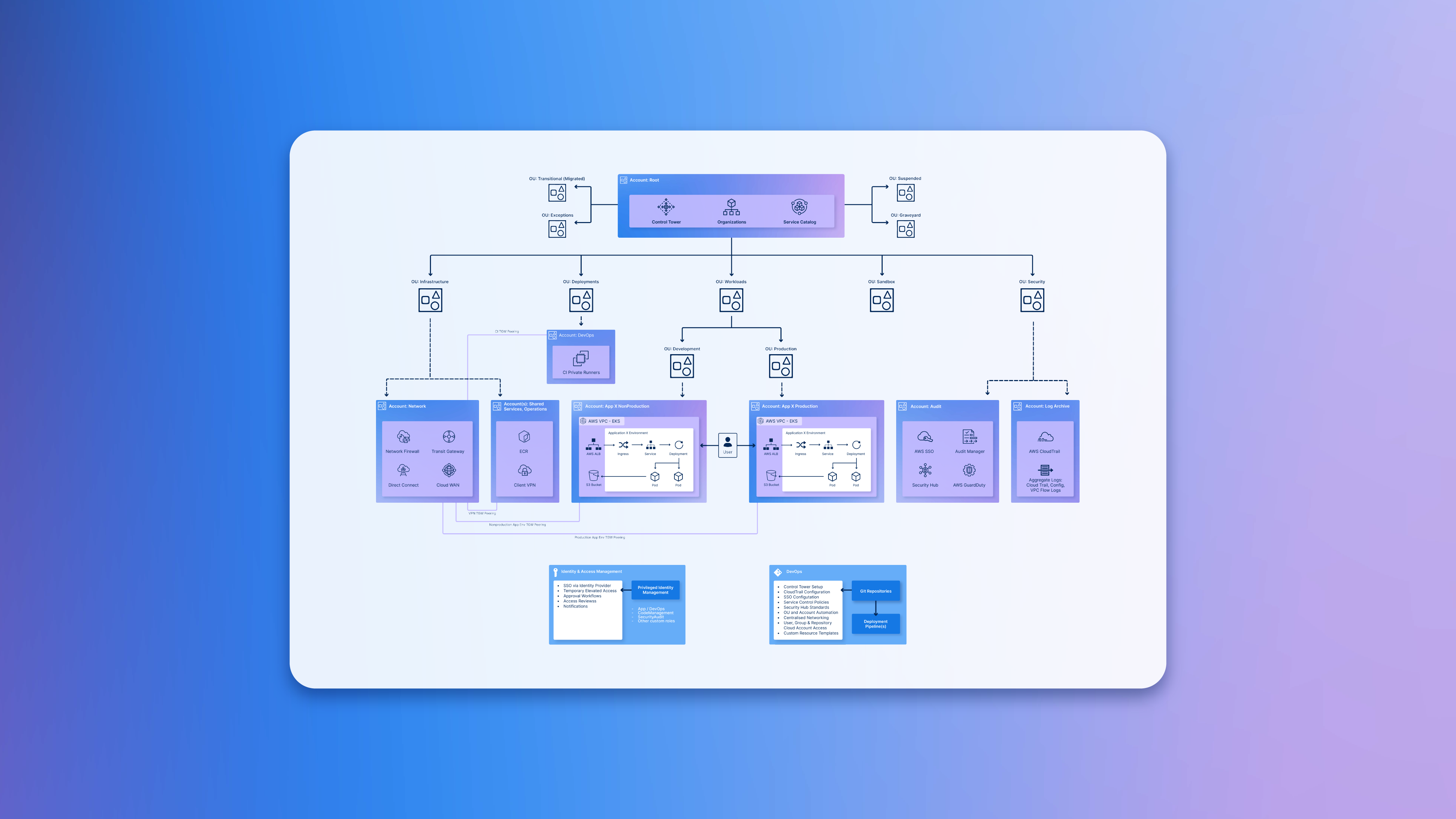
If you’re new to Landing Zones, we advise you to start out with the following reference architecture diagram, as it focuses on delivering cloud setup that adheres to AWS guidelines of multi-account structure, provides with baseline security, identity management and promotes scalability:
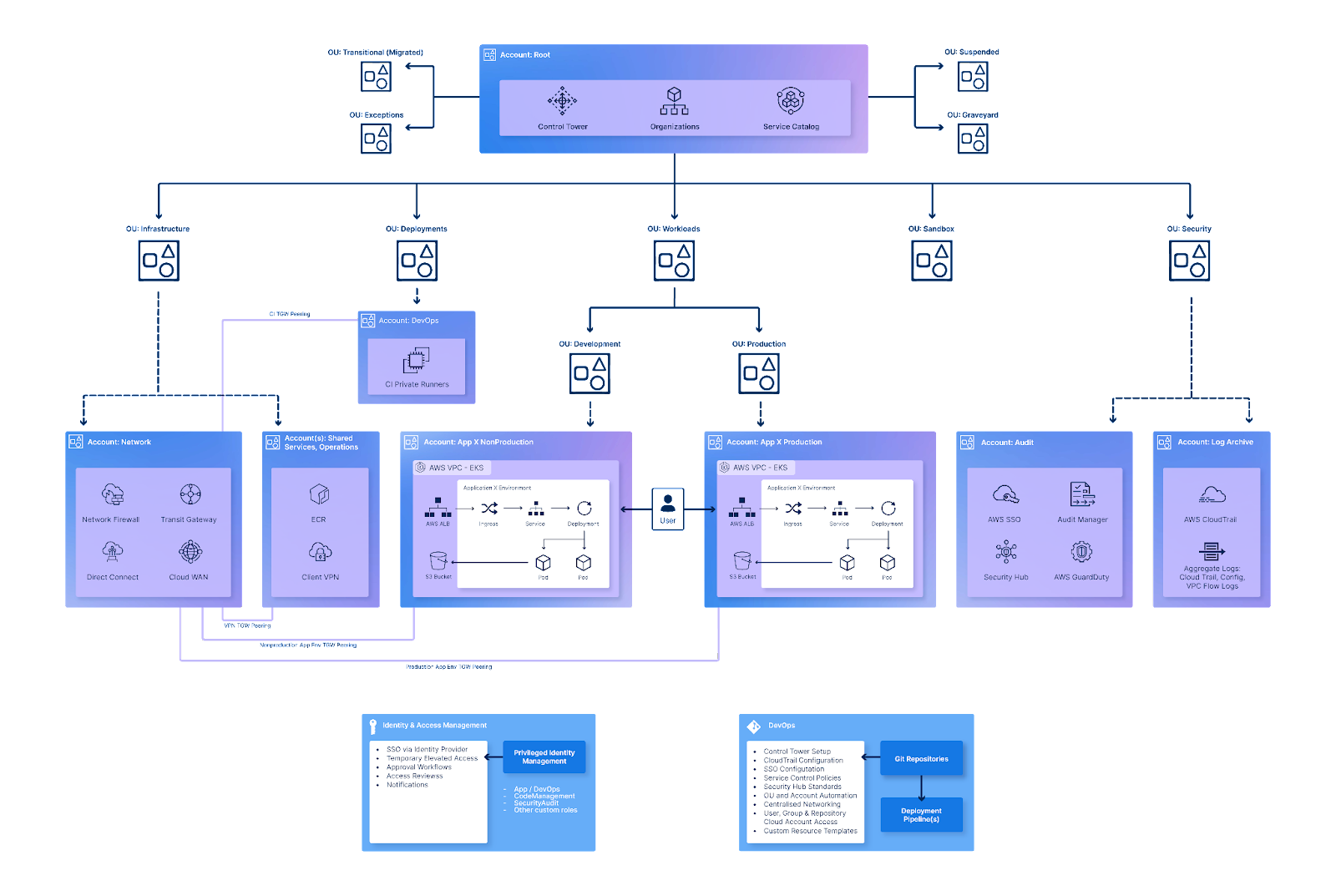
A: AWS account structure: AWS operates on the basis of Organisations, enabling you to systematically organise your AWS accounts into organisational units (OUs). This concept ensures that your workloads stay segregated and logically organised.
B: Initial security baseline, governance, data security and logging: Best practices and tooling that your organisation can implement for audit and logging purposes.
C: Identity and access management: Best practices surrounding any privileged identity management actions, such as SSO, temporary access, and approval workflows.
D: Network Design: Best practices surrounding network design, connectivity, and remote access operations.
E: Optional additional considerations: DevOps practices implemented through infrastructure as code, such as automated deployment, pipeline management and various configurations.
One of the most fundamental design considerations is your AWS account setup for your organisation. Although there are different ways in which your organisation could structure your accounts and organisational units, AWS account structure practise advise on the following multi-account set up:
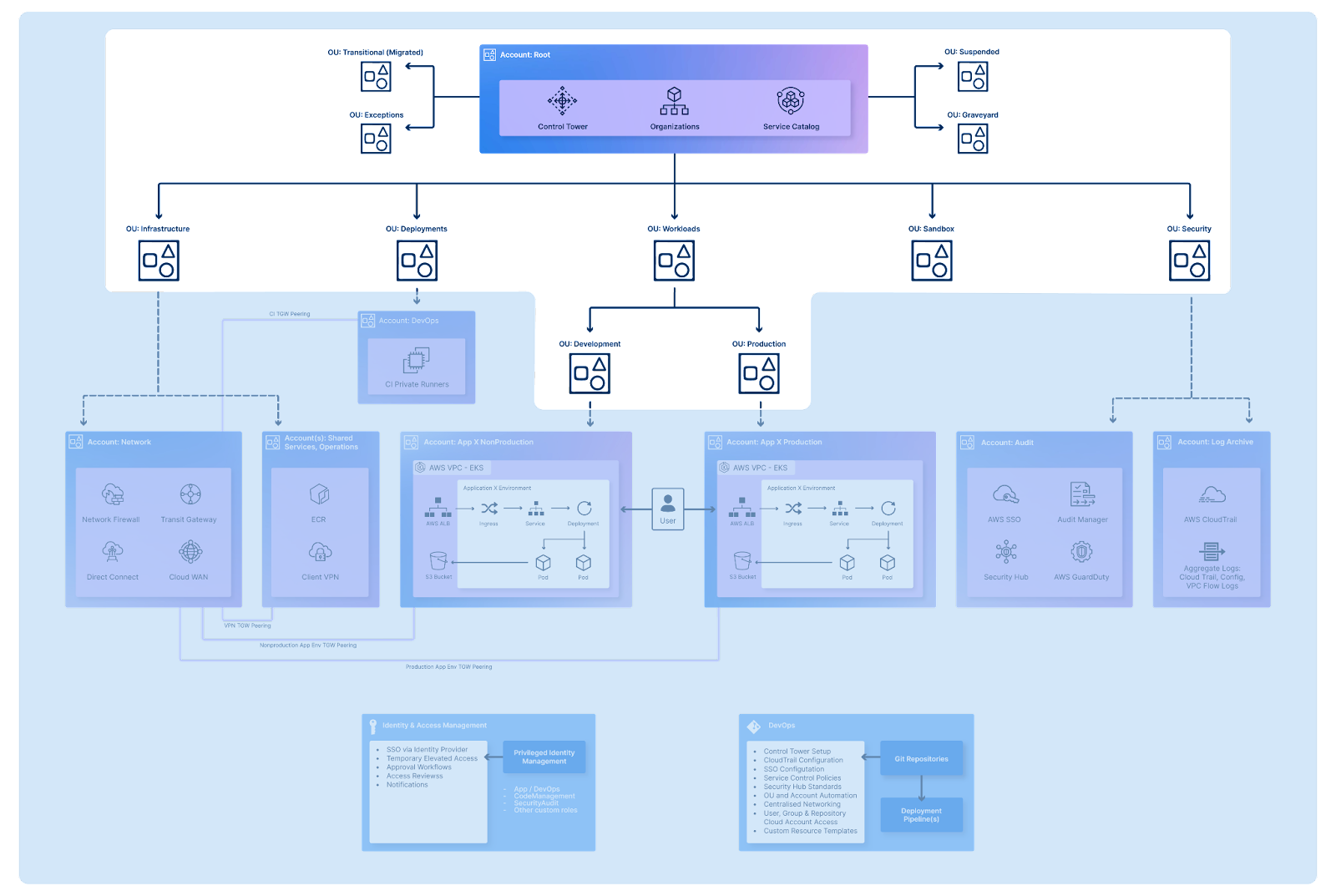
As far as the initial security baseline is concerned, AWS suggests the following split of your Security OU:
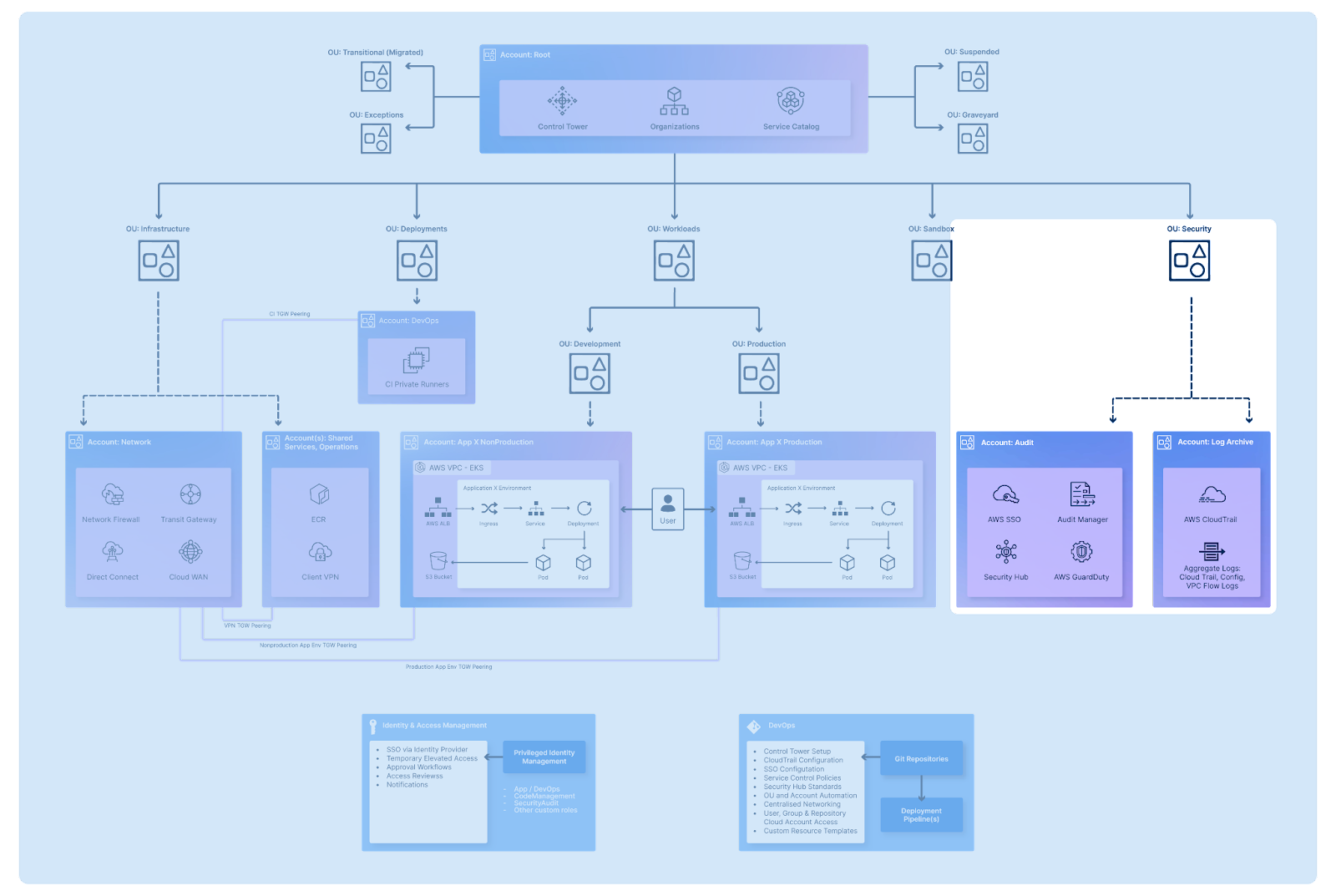
Your AWS-managed security tools, such as GuardDuty or Security Hub, should be managed through the Audit account, enabling you to analyse, understand, and alert on any unexpected activities in your organisation. It is also recommended to include an Archive account—a central logging account aggregating various logs across all of your OUs and tools, such as CloudTrail, Config, or VPC Flow Logs, for centralised and isolated audit of your estate. The creation of both Audit and Archive accounts is provided by default when using AWS Control Tower, the AWS-managed landing zone provisioning service.
Identity and access management design principles concentrate on assessing your organisation’s identity management. The recommended approach is to apply the least privilege principle, which grants the minimum required access. You can also implement temporary elevated identity management through integration of SSO via any chosen Identity Provider.
As far as the Network Design principle is concerned, AWS suggests creating a separate, centrally managed account for networking:
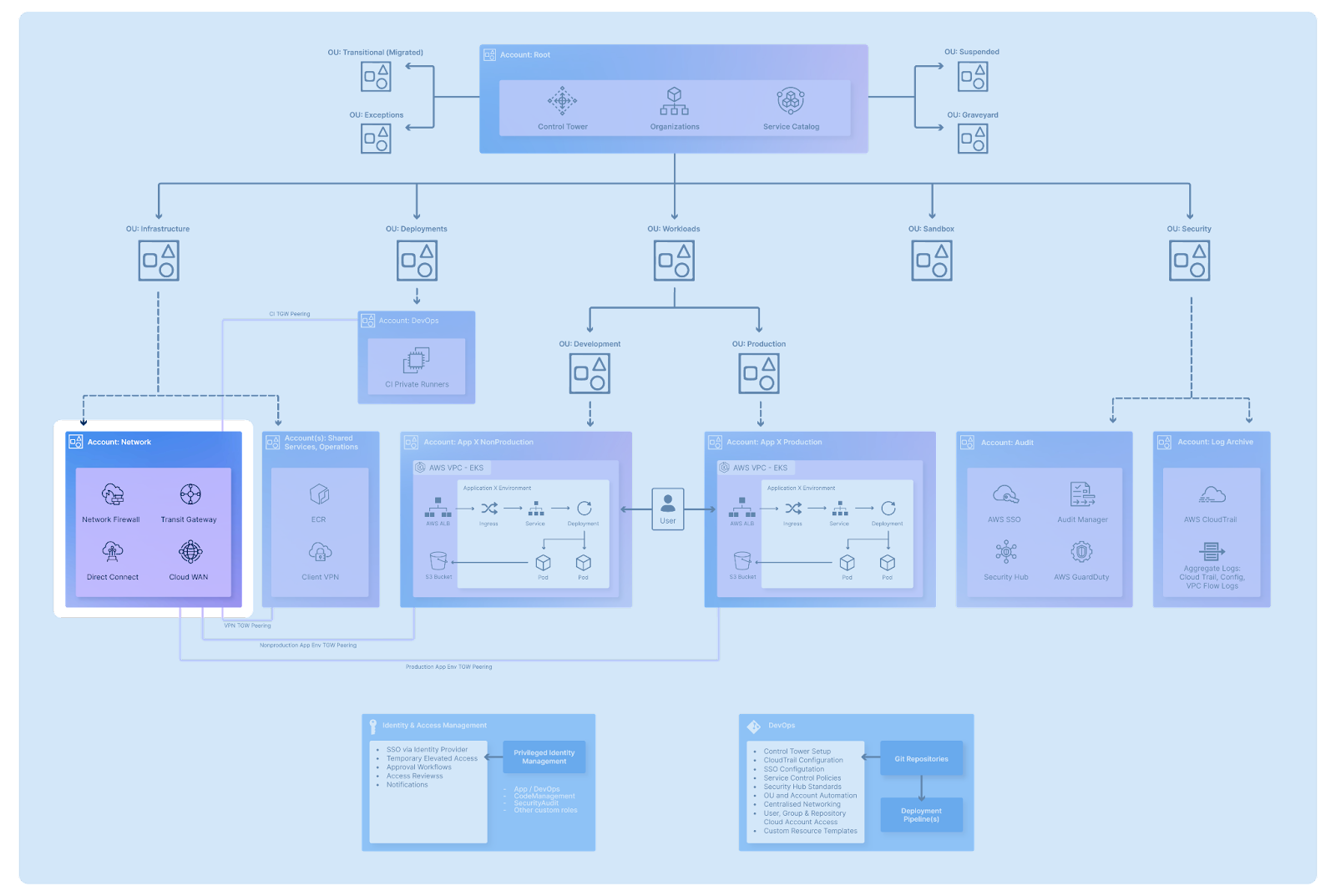
This should involve evaluating your CIDR allocation, as overlapping CIDR ranges within your organisation can present issues related to internal connectivity through Transit Gateways, VPC peering, or VPNs. Additionally, you could implement services such as AWS Network Firewall to implement secure connectivity across services and to on-premise infrastructure.
Additional considerations should include the implementation of various DevOps practices, such as git repository management with a strong access management structure, use of deployment pipelines and any implementation/configuration best practices implemented through infrastructure as code:
It must be mentioned that currently, implementing Landing Zones in AWS may prove to be challenging, either due to the lack of customisation with AWS-managed landing zone solutions or the learning curve and additional cost associated with custom solutions.
Additionally, customisation options can still be limited with the AWS landing zone accelerator, and adding your own elements requires specialist knowledge. As the solution is only CloudFormation-based, companies preferring Terraform or other infrastructure as code tooling may find it adds additional management overhead.
Despite these limitations, AWS Landing Zones can provide a strong starting point for organisations looking to establish a secure, well-architected AWS environment. It's important to evaluate whether the benefits they offer align with your organisation's specific goals and requirements and whether any shortcomings can be addressed or mitigated. Appvia can also help your organisation with the complexities of AWS Landing Zone implementation.
AWS landing zones can be implemented in one of the following ways:
AWS Landing Zones offer best practices for scalable cloud environments, ensuring standardisation, efficiency, security, compliance, and cost management.
Implementing AWS Landing Zones may face hurdles like limited customisation, learning curves, and extra costs. However, they provide a strong foundation for secure cloud environments.
Explore AWS Control Tower, AWS Organisations, or the AWS Landing Zone Accelerator to evolve with your cloud strategy.